GRAFTING TECHNIQUES
Article by:- Hemanth.S
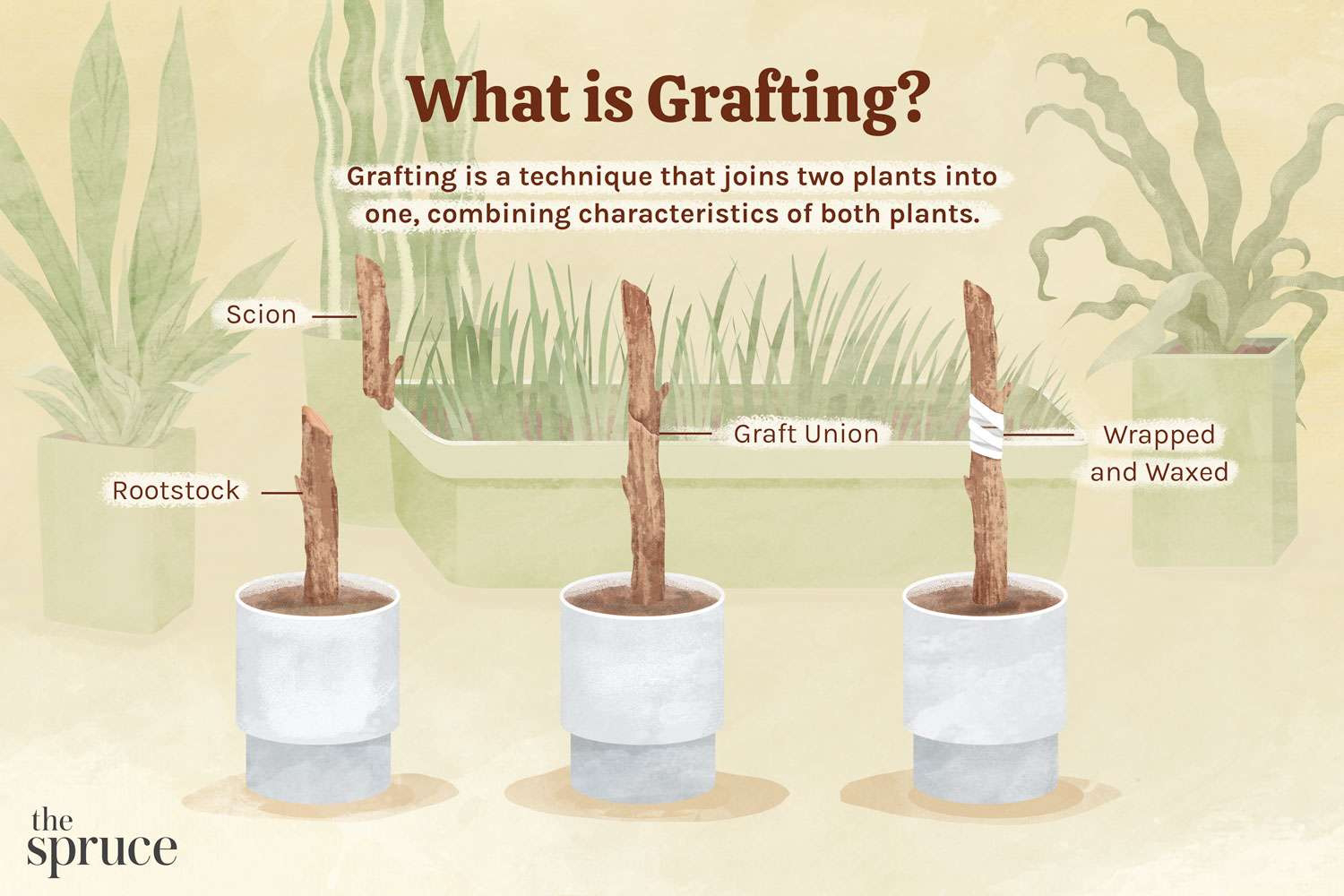
WHAT IS GRAFTING?
Grafting is a horticultural technique used to join plant parts from two or more plants so that they appear to grow as a single plant. The upper part is called as scion and lower called as rootstock.
WHEN TO GRAFT ?
Most of the grafting is done during winter and early spring while both scion and rootstock are still dormant. Winter is the best time for grafting many fruiting and flowering plants.
DIFFERENT STYLES OF GRAFTING
Side-Veneer grafting
Whip-tongue grafting
Cleft grafting
Approach grafting
Splice/ whip grafting
SIDE-VENEER GRAFTING
Mostly this style was used for grafting varieties of camellias and rhododendrons that are difficult to root. Currently this was the most popular way to graft conifers, especially those having a compact or dwarf form. Side grafting is generally done in potted plants.
Cut the root stock as shown in figure in side wise manner, and cut the scion (scion diameter should be smaller than rootstock) in opposite manner to rootstock. Insert the scion part in to rootstock cutting side part and tie the graft union with polythene strip covers tightly.
2. WHIP-TONGUE GRAFTING
This style was used in nursery plants or woody ornamentals. Both scion and rootstock should be equal in diameter (preferably no more than ½ inch in size).
Make similar cut on both the rootstock and scion as shown in diagram. Tie the graft union with polythene cover .after some days the graft union is completed and cut the polythene cover.
3. CLEFT GRAFTING
One of the simplest and most popular grafting style. Cleft grafting is a method for top working both flowering and fruiting trees (apples, cherries, pear and peaches) in order to change varieties. This grafting is usually done during winter and early spring while both scion and rootstock are in dormant stage.
The rootstock used for cleft grafting should be in a range from 1 to 4 inches in diameter and scion should be ¼ inch in diameter. Cut the rootstock centrally and insert the scion into the rootstock and make the graft union.
4. APPROACH GRAFTING
In this type grafting both rootstock and scion should be same size. Both the plants bring together and make the cut and form the union between them after formation of graft union cut upper part of the rootstock and lower part of scion.
In this one both the parents should be grafted and the plants should be near together for good graft union making. This must be performed in the season when plants are in active growth because under such conditions, rapid healing of union takes place.
5. SPLICE/ WHIP GRAFTING
In this type both rootstock and scion should be same diameter. Cut off the rootstock using a diagonal cut ¾ to 1 inch long. Cut off the scion in same manner but in opposite cut should be done. Insert the scion and fit it to rootstock and seal the junction with grafting wax or grafting paint.





Comments
Post a Comment